Masterclasses & Workshops
COSTING
Introduction
This one-day costing course has been specifically developed to acquaint people with product/service costing skills so as to enable them to understand pricing. Course content includes coverage of related topics such as fixed vs variable cost, production/non production related costs, direct vs indirect costs, costing methods such as absorption or ABC costing, batch/service/process costing, etc. Emphasis will be given on practical real life examples rather than theoretical concepts.
This program provides answers to questions such as:
-
What are the costs involved while producing a product or/and offering a service?
-
How do I determine a product/service cost structure in order to price it?
-
Optimum costing and pricing strategies.
Prerequisites
Primary knowledge of basic cost accounting concepts will be helpful but not a pre-requisite in order to attend the course. No advance preparation is required.
Course Benefits
This is a course that can be followed both by a starter as well as the experienced management or/and cost accountant since it combines basic costing principles as well as more advanced practical examples which may help build on the already existing knowledge base of the advanced attendee:
Teaching Method
Live group instruction, examples and case studies, open discussions. Interactive participation is encouraged.
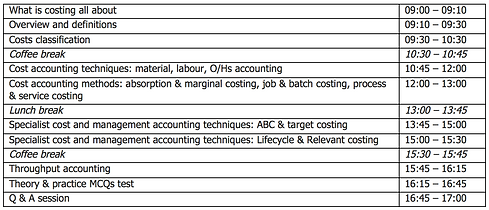
Agenda
Your trainer
Dimitris Chatziapostolou is a chartered certified accountant (FCCA) and a certified compliance officer (AICA) having accumulated a 20+ year extensive international business experience, out of his 6+ year employment in the big 4 audit firm environment (PwC, Arthur Andersen, Deloitte) and 10 years as a CFO (Sony Music, Metlife Alico, Frigoglass). Currently working for SmartAdvisory as a freelance financial consultant in Europe, Asia and the Middle East as well as for StudySmart as a professional qualifications tutor with more than 5,000 training hours of experience.
Qualifications: AICA-Advanced Certificate in Compliance, International Compliance Association (UK), FCCA, Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (UK), MBA, Cardiff Business School-University of Wales (UK), BA (Hons) Business Economics - University of Liverpool (UK)
Course Duration: 1 day – 09.00 – 17.00
Cost classification
-
Explain and illustrate production and non- production costs
-
Describe the different elements of non production costs- administrative, selling, distribution and finance
-
Describe the different elements of production cost- materials, labour and overheads
-
Explain the importance of the distinction between production and non production costs when valuing output and inventories
-
Explain and illustrate with examples classifications used in the analysis of the product/service costs including by function, direct and indirect. fixed and variable, stepped fixed and semi variable costs.
-
Explain and illustrate the use of codes in categorising transaction
-
Describe and illustrate, graphically, different types of cost behaviour
-
Use high/low analysis to separate the fixed and variable elements of total costs including situations involving semi variable and stepped fixed costs and changes in the variable cost per unit
Accounting for material, labour and overheads
-
Accounting for materials (i) Describe the different procedures and documents necessary for the ordering, receiving and issuing of materials from inventory. (ii) Describe the control procedures used to monitor physical and ‘book’ inventory and to minimise discrepancies and losses. (iii) Interpret the entries and balances in the material inventory account. (iv) Identify, explain and calculate the costs of ordering and holding inventory (including buffer inventory). (v) Calculate and interpret optimal reorder quantities. (vi) Calculate and interpret optimal reorder quantities when discounts apply. (vii) Produce calculations to minimise inventory costs when inventory is gradually replenished. (viii) Describe and apply appropriate methods for establishing reorder levels where demand in the lead time is constant. (ix) Calculate the value of closing inventory and material issues using LIFO, FIFO and average methods.
-
Accounting for labour (i) Calculate direct and indirect costs of labour. (ii) Explain the methods used to relate input labour costs to work done. (iii) Prepare the journal and ledger entries to record labour cost inputs and outputs.
-
Accounting for overheads (i) Explain the different treatment of direct and indirect expenses. (ii) Describe the procedures involved in determining production overhead absorption rates. (iii) Allocate and apportion production overheads to cost centres using an appropriate basis. (iv) Reapportion service cost centre costs to production cost centres (including using the reciprocal method where service cost centres work for each other) (v) Select, apply and discuss appropriate bases for absorption rates. (vi) Prepare journal and ledger entries for manufacturing overheads incurred and absorbed. (vii) Calculate and explain the under and over absorption of overheads.
Absorption and marginal costing
-
Explain the importance of, and apply, the concept of contribution
-
Demonstrate and discuss the effect of absorption and marginal costing on inventory valuation and profit determination
-
Calculate profit or loss under absorption and marginal costing
-
Reconcile the profits or losses calculated under absorption and marginal costing
-
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of absorption and marginal costing
Cost accounting methods
-
Job and batch costing: Describe the characteristics of job and batch costing. (ii) Describe the situations where the use of job or batch costing would be appropriate. (iii) Prepare cost records and accounts in job and batch costing situations. (iv) Establish job and batch costs from given information.
-
Process costing (i) Describe the characteristics of process costing. (ii) Describe the situations where the use of process costing would be appropriate. (iii) Explain the concepts of normal and abnormal losses and abnormal gains. (iv) Calculate the cost per unit of process outputs. (v) Prepare process accounts involving normal and abnormal losses and abnormal gains. (vi) Calculate and explain the concept of equivalent units.
-
Service/operation costing (i) Identify situations where the use of service/operation costing is appropriate. (ii) Illustrate suitable unit cost measures that may be used in different service/operation situations. (iii) Carry out service cost analysis in simple service industry situations.[s]
Activity based costing
-
Identify appropriate cost drivers under ABC
-
Calculate costs per driver and per unit using ABC
-
Compare ABC and traditional methods of overhead absorption based on production units, labour hours or machine hours
Target costing
-
Derive a target cost in manufacturing and service industries
-
Explain the difficulties of using target costing in service industries
-
Suggest how a target cost gap might be closed
Life-cycle costing
-
Identify the costs involved at different stages of the life-cycle
-
Derive a life cycle cost in manufacturing and service industries
-
Identify the benefits of life cycle costing